𝐀𝐝𝐝𝐢𝐭𝐢𝐯𝐞 𝐌𝐚𝐧𝐮𝐟𝐚𝐜𝐭𝐮𝐫𝐢𝐧𝐠- 𝐕𝐚𝐭 𝐩𝐡𝐨𝐭𝐨𝐩𝐨𝐥𝐲𝐦𝐞𝐫𝐢𝐳𝐚𝐭𝐢𝐨𝐧- 𝐁𝐥𝐨𝐠 𝟐
What is Vat Photopolymerization?
References:
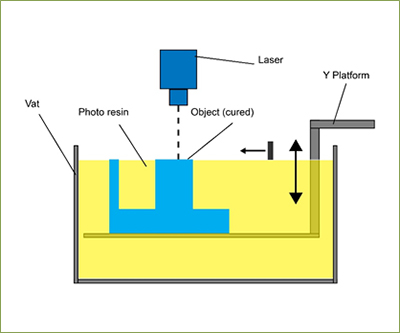
Imagine dipping a brush into a vat of liquid plastic and then using light to solidify the plastic into desired shapes, layer by layer. That's the basic principle behind vat photopolymerization. This technology utilizes a vat containing liquid photopolymer resin, which is essentially a mixture of monomers, oligomers, and a photoinitiated. When exposed to light, the photoinitiated triggers the polymerization reaction, causing the monomers and oligomers to link together and form a solid polymer structure.
 |
| [1] |
Process Steps:👈
- Model Preparation: 3D models are created using CAD software and converted into specific file formats compatible with the printing machine.
- Vat Filling: The printing platform is lowered into the vat filled with liquid photopolymer resin.
- Layer-by-Layer Curing: A light source (laser in SLA, projector in DLP) projects light onto the surface of the resin, selectively curing the desired areas based on the model's digital slices.
- Platform Movement: After each layer is cured, the platform is lowered by the machine's predetermined layer height, and the process repeats until the entire model is solidified.
- Post-processing: Once printing is complete, the object is removed from the platform and undergoes post-processing steps like rinsing, UV curing, and support removal.
Advantages:👈
- High Resolution: Vat photopolymerization produces parts with exceptional surface finish and high resolution, enabling intricate details and smooth surfaces.
- Wide Material Range: Diverse photopolymer resins are available, offering various properties like stiffness, flexibility, transparency, and biocompatibility.
- Fast Printing Speeds: Compared to other 3D printing technologies, vat photopolymerization can produce objects relatively quickly, especially for smaller parts.
- Minimal Material Waste: Unused resin can be recycled and reused, minimizing material waste compared to other additive manufacturing methods.
Disadvantages:
- Limited Build Volume: Vat size determines the maximum build volume, restricting the size of printable objects.
- Shrinkage and Distortion: Photopolymer resins can experience shrinkage and distortion during the printing process, requiring careful calibration and support structures.
- Limited Material Properties: While diverse resins are available, some properties like strength and temperature resistance may not be as high as other materials used in traditional manufacturing.
- Safety Precautions: Handling photopolymer resins requires proper safety measures as they can be irritants and harmful if ingested or inhaled.
Defects:👈
- Layer Lines: Visible lines on the surface of the object due to the layer-by-layer nature of the process.
- Support Marks: Markings left on the object where support structures were attached.
- Incomplete Curing: Insufficient curing can lead to weak and brittle parts.
- Delamination: Layers of the object can separate due to improper curing or adhesion.
Applications:👈
Vat photopolymerization finds applications in various industries, including:
- Prototyping: Creating realistic and functional prototypes for testing and design iteration.
- Jewelry Design: Printing intricate and detailed jewelry pieces with high accuracy.
- Dental and Medical: Fabricating dental models, surgical guides, and medical implants.
- Figurines and Collectibles: Producing high-quality collectibles with fine details.
- Functional Parts: Creating functional parts with specific mechanical and thermal properties.
Conclusion:
Vat photopolymerization is a powerful and versatile technology revolutionizing design and manufacturing across various industries. Its ability to produce high-resolution parts with diverse material properties makes it an invaluable tool for engineers, designers, and artists alike. As this technology continues to evolve with advancements in materials and printing techniques, we can expect even more exciting applications and possibilities in the future.
***In the upcoming blogs we will discuss the in depth of every AM techniques***
Note: The images are taken from the google images for better understanding of the readers and gave the appropriate references below....
***LIKE, SHARE, COMMENT***






Comments
Post a Comment